Hot Girl làm Vợ. 40 tập 44:00 phút 24.554 lượt năm nhâm thìn Việt Nam. Gói cước: Miễn phí. Thể loại: Việt Nam. Diễn viên: Đặng Thu Thảo, Trương nam Thành, Quốc Cường, Thanh Trúc, Huỳnh Anh Tuấn, Hoàng Yến Chib
Domain: tv24.vn
Liên kết: https://tv24.vn/chi-tiet/19544/hot-girl-lam-vo/2
Hot girl làm bà xã Tập 38
Phim Lẻ - Phim Chiếu Rạp; Phim Việt Nam. Chỉ là Ảo Ảnh (THVL1) - Trọn bộ - Phim Việt Nam; tía Ơi bà bầu Có Về không (Trọn Bộ) Phim Vòng Vây Hoa Hồng; Phim Ông trùm (Xã Hội Đen) mùi hương Đồng Nội - Hoài Linh (
Chi ngày tiếtHot girl làm vợ Tập 39
Xem trọn cỗ : https://www.dailymotion.com/playlist/x643q7Hot Girl Làm vk - Phim nước ta (Phim Đặc sắc đẹp HD)Xem Phim hot girl lam vo tron bo phim...
Bạn đang xem: Top 10 phim hot girl làm vợ tập 40 trọn bộ
Hot girl làm vợ Tập 40 tập cuối
Hot girl làm bà xã Tập 40 tập cuối... Sao Vàng. Sign in; Home; Videos Videos. Browse Categories; New; Popular; ... Trọn cỗ - Phim Việt Nam; tía Ơi bà bầu Có Về không (Trọn Bộ) Phim Vòng Vây Hoa Hồng; Phim Ông
Chi tiếtHot girl làm bà xã Tập 12b
Phim Lẻ - Phim Chiếu Rạp; Phim Việt Nam. Chỉ là Ảo Ảnh (THVL1) - Trọn cỗ - Phim Việt Nam; tía Ơi mẹ Có Về không (Trọn Bộ) Phim Vòng Vây Hoa Hồng; Phim Ông trùm (Xã Hội Đen) hương thơm Đồng Nội - Hoài Linh (
Chi ngày tiếtbạn có những thắc mắc hoặc những thắc mắc cần mọi bạn trợ góp hay hỗ trợ hãy gửi câu hỏi và vấn đề đó cho chúng tôi. Để shop chúng tôi gửi vụ việc mà chúng ta đang chạm mặt phải cho tới mọi người cùng tham gia đóng gop ý kiếm giúp bạn... Gửi thắc mắc & Ý kiến góp sức »
















Trực tuyến đường | 9:00 | Thánh Lễ Khánh Thánh và Cung Hiến...




Bài viết mới
 Công Thông Tin tư vấn - Hỏi Đáp - Tra cứu giúp - tra cứu Kiếm Trực Tuyến
Công Thông Tin tư vấn - Hỏi Đáp - Tra cứu giúp - tra cứu Kiếm Trực Tuyến

Trang chuyên tứ vấn cung cấp hỏi đáp, tra cứu với tìm kiếm tin tức đọc giả đã quan tâm. Chúng tôi luôn mong muốn đóng góp chủ kiến và được sát cánh đồng hành cùng những bạn.
Bài viết ngay sát đây
Menu
Danh mục và Tìm kiếm
danh mục --- Chọn danh mục ---Nhiếp Ảnh, Dựng Phim(3)Hôn nhân gia đình(4)Nuôi dạy dỗ Con(5)Phong phương pháp sống(13)Sức khỏe giới tính(8)Công Nghệ Thông Tin(2)Sales cung cấp Hàng(5)Kỹ năng mềm(6)Thiết kế(8)Tin Học(3)Ngoại Ngữ(5)Giáo dục(4) tìm kiếm for:Follow Us
Thiết kế vày www.hoidap.edu.vn
1 INTRODUCTION
Lung volumes are subdivided into static và dynamic lung volumes. Static lung volumes are measured by methods which are based on the completeness of respiratory manoeuvres, so that the velocity of the manoeuvres should be adjusted accordingly. The measurements taken during fast breathing movements are described as dynamic lung volumes và as forced inspiratory & expiratory flows.
1.1 Static lung volumes and capacities
The volume of gas in the lung & intrathoracic airways is determined by the properties of lung parenchyma and surrounding organs and tissues, surface tension, the force exerted by respiratory muscles, by lung reflexes and by the properties of airways. The gas volumes of thorax & lung are the same except in the case of a pneumothorax. If two or more subdivisions of the total lung capacity are taken together, the sum of the constituent volumes is described as a lung capacity. Lung volumes và capacities are described in more detail in § 2.
1.1.1 Determinants
Factors which determine the size of the normal lung include stature, age, sex, body mass, posture, habitus, ethnic group, reflex factors and daily activity pattern. The cấp độ of maximal inspiration (total lung capacity, TLC) is influenced by the force developed by the inspiratory muscles (disorders include e.g. muscular dystrophy), the elastic recoil of the lung (disorders include e.g. pulmonary fibrosis và emphysema) & the elastic properties of the thorax and adjacent structures (disorders include e.g. ankylosis of joints). The cấp độ of maximal expiration (residual volume, RV) is determined by the force exerted by respiratory muscles (disorders include e.g. muscle paralysis), obstruction, occlusion & compression of small airways (disorders include e.g. emphysema) và by the mechanical properties of lung and thorax (disorders include diffuse fibrosis, kyphoscoliosis).
Assessing the total lung capacity is indispensable in establishing a restrictive ventilatory defect or in diagnosing abnormal lung distensibility, as may occur in patients with emphysema. Measurements of lung volumes are also essential in interpreting data on lung elastic recoil pressure, instantaneous ventilatory flows, airways resistance, và the transfer factor of the lung, since these are all volume dependent.
1.1.2 Restrictive ventilatory defects
Static lung volumes may be diminished by disorders which restrict lung expansion (restrictive ventilatory defects), such as neuromuscular disorders, diseases of the chest wall & abdomen, disorders of the pleural space, increase in lung stiffness, and decrease in the number of available alveolar units (lung resection, atelectasis, scars).
A restrictive ventilatory defect is best described on the basis of a reduced TLC rather than from vital capacity measurements. The vital capacity, i.e. the volume change between RV và TLC, may be diminished by both restrictive & obstructive ventilatory defects; in the latter case it is due to an increase in residual volume due to (premature) airways closure (gas trapping) và airflow limitation at low lung volumes <1, 2>, leading khổng lồ incomplete lung emptying. However, in small airways disease the RV is increased with no change in TLC; accordingly the VC is reduced (with a proportionate decrease in FEV1 <3>). Hence the vital capacity alone is of little use in discriminating between restrictive, obstructive và mixed ventilatory defects. In some cases of cystic fibrosis, which primarily affects the airways, temporary decreases in TLC have been described, possibly due lớn partial atelectasis <4>.
1.1.3 Hyperinflation
The total lung capacity may be abnormally large in acromegaly & in the case of increased lung distensibility. In the latter situation RV & the functional residual capacity (FRC) are also increased, whereas TLC tends khổng lồ decrease. The term hyperinflation has been proposed khổng lồ describe the increase in FRC <5>; however, it is also frequently used lớn describe increases in TLC or RV. Hyperinflation is usually associated with an obstructive ventilatory defect (see § 1.2.2), but the relationship between the increased FRC và the lowered FEV1 is weak <6>.
1.2.1 Determinants
The ability lớn move air rapidly in và out of the lungs is essential for normal activity, và any diminution of more than minimal extent will usually cause breathlessness on exertion và hence reduce the capacity for exercise. Ventilatory impairment can arise from changes in the nervous system, the skeleto-muscular system, the skin and subcutaneous tissues, the lungs or the inhaled gas. However the commonest cause is narrowing of the airways. The impairment can be detected by dynamic spirometry, which constitutes the first stage in the assessment of respiratory function. Subsequent stages include consideration of mechanisms, the amount of function which remains, the cause of the condition & the means for its alleviation.
Dynamic lung volumes and flows are assessed during forced inspiration or expiration, or during forced breathing when maximal effort is applied throughout the respiratory manoeuvre. In this it differs from the measurement of static lung volumes where the maximal effort is generated only at the beginning & end of the manoeuvre. The results of dynamic spirometry are usually expressed in terms of the relationships of inspired or expired volume khổng lồ time as described by the volume-time curve (spirogram: fig. 1). They are also expressed as the relationship of maximal flow to lung volume described by the flow-volume curve (fig. 2).
Xem thêm: Giờ Làm Việc Ngân Hàng Acb Làm Việc Đến Mấy Giờ, Giờ Làm Việc Ngân Hàng Acb Mới Nhất Năm 2023
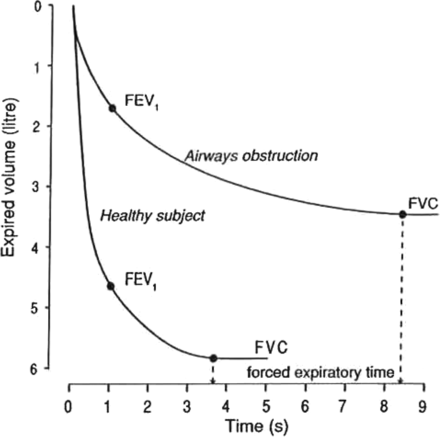
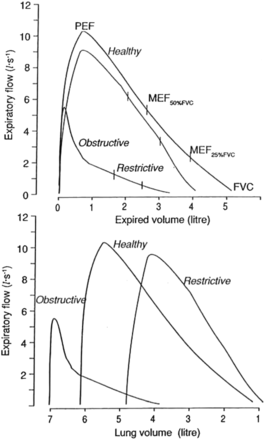
Figure 3–
Schematic representation of static lung volumes và capacities. Modified with permission from <41>. See text for definitions.